The Ultimate Guide about Buying Signals : definition + examples + tools
Identifying the right moment to approach a prospect can be like finding a needle in a haystack. Competition between sales team have never been higher than now. So, you have to stand out by being smart. It's all about "momentum". The right company, the right contact at the right time.
Buying signals is a huge source of data which help you to convert your deals faster.
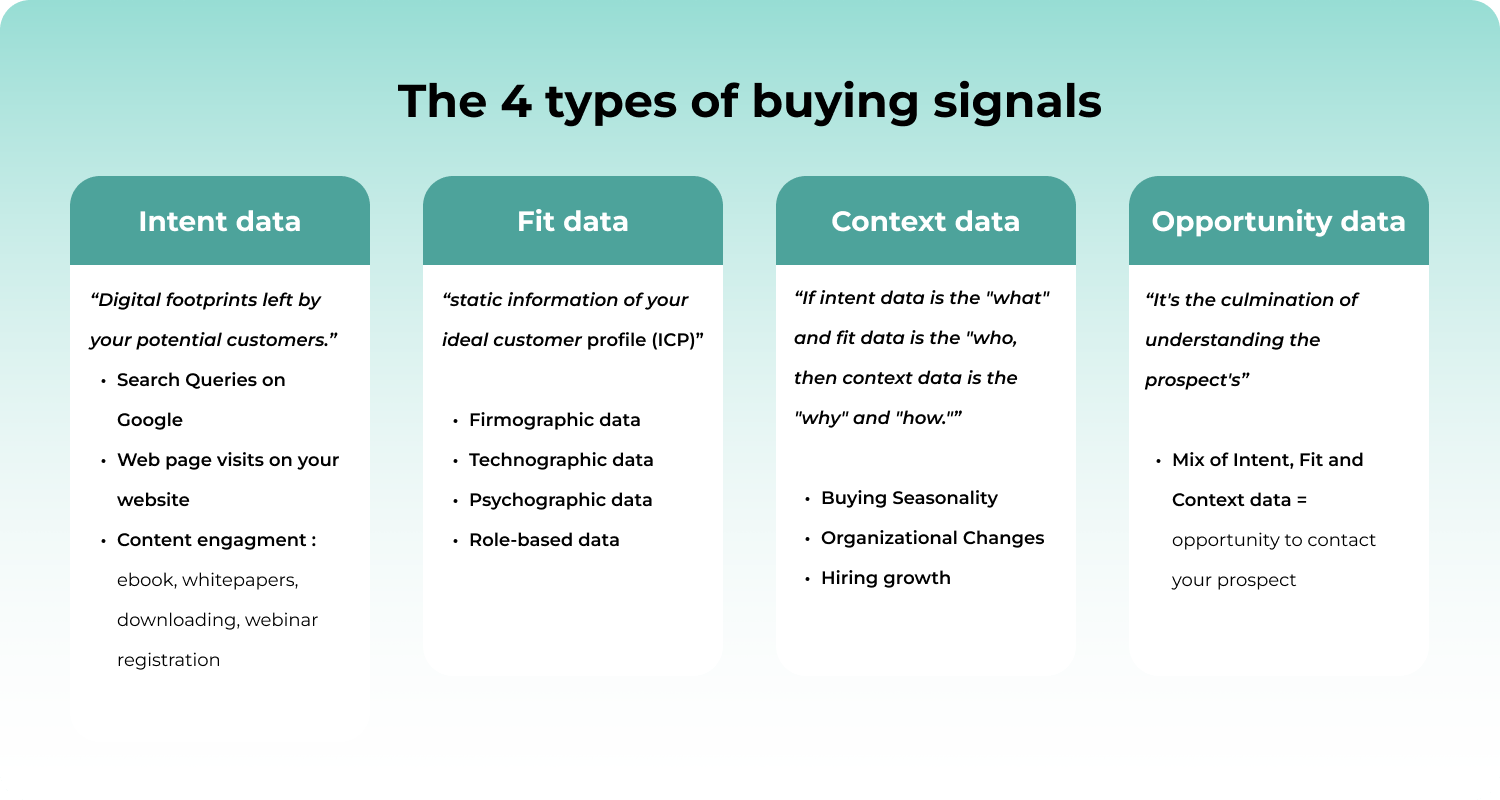
How do we identify those crucial buying signals that indicate a lead is not just interested, but ready to purchase? The answer lies in the confluence of four distinct types of data:
- Intent data
- Fit data
- Context data
- Opportunity data.
Focusing on the following categories, you can establish a robust strategy that enables you to identify the highest-quality prospects at the most opportune time.
Let’s dive into each of these to gain a comprehensive understanding.
Intent Data: understanding what prospects Want
Think of intent data as the digital footprints left by your potential customers. These are the clues that reveal what a prospect is interested in, or actively searching for. Collecting intent data often involves tracking online activities like:
- Search Queries: What kind of terms are prospects using in search engines that relate to your product or service?
Example: A user types "best project management software for architects" into a search engine. This search query strongly suggests that the individual is in the market for specialized project management software and is likely in the consideration phase of the buying cycle. - Web Page Visits: Are they spending time on your website or on competitor sites? What pages are they viewing?
Example: An HR manager from a tech firm visits your website and checks out multiple pages, including the 'Pricing', 'Features', and 'Customer Testimonials' sections of your HR software solution. This pattern of webpage visits indicates a serious interest and could even imply that the manager is comparing your product to competitors. - Content Engagement: Are they downloading white papers, signing up for webinars, or reading related blog posts?
Example: A marketing executive spends time reading a long-form blog post on your site about the "ROI of social media advertising," shares it on LinkedIn, and then downloads a related eBook. This type of engagement with your content shows that the executive is not only interested, but also finds the information valuable enough to share and download for further reading.
The value in intent data lies in its immediacy. Someone actively searching for a product or solution you offer is arguably a marketing qualified lead than someone who fits your ideal customer profile but isn't actively looking.
There are a plethora of tools that can help you gather and analyze intent data. Platforms like ZoomInfo, Bombora or HubSpot provide intent data gathered from multiple sources across the web, helping you understand not just how users interact with your content, but also how they engage with competitor sites and other relevant online platforms. These tools can give you a more holistic understanding of your target audience's intent, enabling more effective, targeted marketing campaigns.
Fit Data: The Right Customer for Your Product
What is Fit Data?
In the simplest terms, Fit data refers to static information that tells you how well a prospect or customer aligns with your ideal customer profile (ICP). Unlike dynamic intent or behavioral data, fit data is generally constant. It's the fundamental "who" in the equation that includes "what" (intent data) and "how" (engagement data).
The Different Types of Fit Data
Firmographic Data
Firmographic data is the B2B equivalent of demographic data in B2C marketing. This includes details like:
- Company Size: Number of employees, revenue, etc.
- Industry: Sector or niche the company operates in.
- Location: Geographical location of the company's headquarters or other offices.
- Organizational Structure: Whether it’s a startup, SMB, or an enterprise.
Technographic Data
Technographic data gives you insights into a company's tech stack, helping you understand what software and hardware solutions they're already using. This can include:
- CRM Software: Salesforce, HubSpot, etc.
- Marketing Automation Tools: Marketo, Pardot, etc.
- E-commerce Platforms: Shopify, Magento, etc.
Psychographic Data
While not as straightforward to gather in a B2B context as it is in B2C, psychographic data can still offer valuable insights. This can include:
- Company Culture: Innovative vs. traditional, risk-taking vs. conservative, etc.
- Pain Points: Common challenges that the company or decision-makers face.
- Goals and Objectives: Short-term and long-term business goals.
Role-based Data
This refers to the information specific to the individuals within the organizations you are targeting:
- Job Titles: CEO, CMO, Project Manager, etc.
- Responsibilities: Decision-making authority, areas of influence, etc.
- Level of Seniority: Entry, middle-management, executive, etc.
How to Use Fit Data Effectively
- Segmentation: Divide your audience based on Fit data to craft more targeted and relevant messaging.
- Personalization: Integrate fit data with behavioral and intent data to create hyper-personalized outreach campaigns.
- Sales Alignment: Share Fit data insights with your sales team to help them prioritize and tailor their pitches.
- Competitive Analysis: Use technographic data to understand your competitors' market penetration and strategize accordingly.
- Content Strategy: Use psychographic and role-based data to create content that addresses specific pain points and objectives
Tips : You can find all information on professional social network like LinkedIn, Wappalyzer, or job board like indeed. You can connect LeverGrow to centralize all sources in your CRM.
Context Data: The Surrounding Circumstances
If intent data is the "what" and Fit data is the "who," then context data is the "why" and "how." Context data encompasses all additional circumstances or behaviors that offer added insights into a prospect's needs or situation.
For instance:
- Buying Seasonality: Are there particular times of the year when they are more likely to buy?
- Organizational Changes: Mergers, acquisitions, fundraising or leadership changes can all act as triggers for purchasing decisions.
- Employees lay-off or hiring growth : do they have many open positions ?
Context data provides you with the bigger picture, enabling a more consultative and tailored approach to sales. CRM platforms can be helpful in aggregating such data points over time.
Opportunity Data: The Right Time and Place
Opportunity data blends elements from the previous three categories to pinpoint the most opportune moments for conversion. It's the culmination of understanding the prospect's intent, fit, and context to accurately gauge their readiness to buy. Knowing when a contract is up for renewal or when a company has secured funding can serve as strong indicators that it's the right time to make your move.
This type of data often involves real-time alerts and triggers that inform you of a prospect's activities and conditions that favor a sale. Think of it as your go-ahead signal. It's the green light you've been waiting for, telling you that now is the time to strike while the iron is hot.
Advice from LeverGrow expert :
It’s hard to collect all data because you have to maintain many sources. Look for an enrichment data solution that collect in real-time all information. Then, the key is to centralize this data in a CRM like Salesforce or HubSpot. Doing so ensures that your sales, marketing, and customer service teams all have real-time access to the same insights. This unified view allows for quicker, more targeted actions, boosting your chances of closing deals. In short, don't just track buying signals—centralize them in a CRM to turn those signals into successful conversions.
Conclusion
The secret sauce of a high-converting sales strategy lies in the intelligent use of various data types. Intent data reveals what your prospects want, Fit data tells you if they're the right customers for your product, context data gives you the broader circumstances, and opportunity data tells you when to make your move. When harmonized, these four types of data offer an unparalleled advantage in identifying genuine buying signals. So go ahead, equip your sales toolkit with these data types, and you'll be well on your way to converting prospects into happy customers.

